Own Funds and capital
For the purposes of calculating minimum capital requirements, according to Regulation (EU) 575/2013 and subsequent amendments, which enter into force on June 27, 2019 (CRR), the elements and instruments of Tier 1 capital are defined as the sum of Common Equity Tier 1 capital (CET1) and additional Tier 1 capital (AT1), as defined in Part Two, Title I, Chapters I to III of the CRR, as well as their corresponding deductions, in accordance with Articles 36 and 56, respectively.
Also considered are the elements of Tier 2 capital defined in Part Two of Chapter IV, Section I of the CRR. The deductions defined as such in Section II of the same Chapter are also considered.
Below is the amount of total eligible capital, net of deductions, for the different items making up the capital base as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, in accordance with the requirements for the disclosure of information related to regulatory own funds established by the Commission's Implementing Regulation (EU) No 1423/2013 of December 20, 2013:
Amount of capital (CC1)
Million Euros
| Reference to template CC2 (1) | 12-31-2019 | 12-31-2018 (2) |
|---|---|---|
| a) Capital and share premium | 27,259 | 27,259 |
| b) Retained earnings | 26,960 | 23,773 |
| c) Other accumulated earnings and other reserves | (7,157) | (7,143) |
| d) Minority interests | 4,404 | 3,809 |
| e) Net interim attributable profit | 1,316 | 3,188 |
| Common Equity Tier 1 Capital before other regulatory adjustments | 52,783 | 50,887 |
| f) Additional value adjustments | (302) | (356) |
| g) Intangible assets | (6,803) | (8,199) |
| h) Deferred tax assets | (1,420) | (1,260) |
| i) Fair value reserves related to gains o losses on cash flow hedges | 69 | 35 |
| j) Expected losses in equity | - | - |
| k) Profit or losses on liabilities measured at fair value | (24) | (116) |
| l) Direct and indirect holdings of own instruments | (484) | (432) |
| m) Securitizations tranches at 1250% | (25) | (34) |
| n) Other CET1 deductions | (142) | (211) |
| Total Common Equity Tier 1 regulatory adjustments | (9,130) | (10,573) |
| Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) | 43,653 | 40,313 |
| o) Equity instruments and AT1 share premium | 5,280 | 4,863 |
| p) Items referred in Article 486 (4) of the CRR | 120 | 142 |
| q) Qualifying Tier 1 capital included in consolidated AT1 capital (including minority interests not included in row d) issued by subsidiaries and held by third parties) | 648 | 629 |
| Additional Tier 1 before regulatory adjustments | 6,048 | 5,634 |
| Total regulatory adjustments of Additional Tier 1 | - | - |
| Additional Tier 1 (AT1) | 6,048 | 5,634 |
| Tier 1 (Common Equity Tier 1 + Additional Tier 1) | 49,701 | 45,947 |
| r) Equity instruments and Tier 2 share premium | 3,064 | 3,768 |
| s) Admissible shareholders' funds instruments included in consolidated Tier 2 issued by subsidiaries and held by third parties | 4,690 | 4,409 |
| -Of which: instruments issued by subsidiaries subject to ex-subsidiary stage | 921 | 37 |
| t) Credit risk adjustments | 550 | 579 |
| Tier 2 before regulatory adjustments | 8,304 | 8,756 |
| Tier 2 regulatory adjustments | - | - |
| Tier 2 | 8,304 | 8,756 |
| Total Capital (Total capital = Tier 1 + Tier 2) | 58,005 | 54,703 |
| Total RWA's | 364,448 | 348,264 |
| CET 1 (phased-in) | 11.98% | 11.58% |
| CET 1 (fully loaded) | 11.74% | 11.34% |
| TIER 1( phased in) | 13.64% | 13.19% |
| TIER 1( fully loaded) | 13.37% | 12.91% |
| Total Capital (phased in) | 15.92% | 15.71% |
| Total Capital (fully loaded) | 15.41% | 15.45% |
- (*) As of December 31, 2019, the difference between phased-in and fully loaded ratios arises from the transitional treatment of certain capital elements, mainly the impact of IFRS9, to which the Group has voluntarily adhered (in accordance with Article 473 bis of the CRR). See paragraph 2.3 for more information on the transitional impact of IFRS9.
- (1) Reference to regulatory balance sheet items (CC2) reflecting the different items described.
- (2) As a result of the amendment to IAS 12 "Income Tax" as explained in Note 2.3 of the Group's Consolidated Financial Statements, and in order to make the information comparable, the information for the 2018 financial year has been restated, with no impact on either consolidated equity or regulatory capital
As of December 31, 2019, Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) phased-in3 stood at 11.98% (with a fully loaded ratio of 11.74%), including the impact of the first application of IFRS 16 which entered into force on January 1, 2019 (-11 basis points), which represents a growth of 40 basis points from December 2018, mainly supported by the profit generation, net of dividend payments and remuneration of contingent convertible capital instruments (hereinafter CoCos), nothwithstanding the moderate growth of risk-weighted assets.
It should be noted that the impairment of the goodwill in the United States recognized by the Group amounting to €1,318 million has no impact on the regulatory own funds.
The Additional Tier 1 phased-in capital (AT1) stood at 1.66% at December 31, 2019. In this regard, BBVA S.A. carried out an issuance of €1.0 billion CoCos, registered at the Spanish Securities Market Commission (CNMV) and another issue of the same type of instruments, registered in the Securities Exchange Commission (SEC), for USD1.0 billion.
On the other hand, in February 2020, the CoCos issuance of €1.5 billion issued in February 2015 will be amortized. As at December 31 2019, it is no longer included in the capital ratios.
Finally, in terms of issues eligible as Tier 2 capital, BBVA S.A. issued a €750 million subordinated debt and carried out the early redemption of two subordinated debt issues; one for €1.5 billion redeemed in April 2019, and another issued in June 2009 by Caixa d'Estalvis de Sabadell with an outstanding nominal amount of €4.9 million and redeemed in June 2019.
With regard to the other subsidiaries of the Group, BBVA Mexico carried out a Tier 2 issuance of USD 750 million and partially repurchased two subordinate issuances ($250 million due in 2020 and $500 million due in 2021). For its part, Garanti BBVA issued another Tier 2 issuance of TRY 253 million.
All of this, together with the evolution of the remaining elements eligible as Tier 2 capital, set the Tier 2 phased-in ratio at 2.28% as of December 31st, 2019. In addition, in the first months of 2020, two subordinated debt issuances eligible as Tier 2 were issued, one of €1.0 billion issued by BBVA, S.A. and another of TRY 750 million issued by Garanti BBVA. These issues will be included in the capital ratios for the first quarter of 2020 with an estimated impact of approximately +28 basis points on the Tier 2 ratio.
Annual evolution of the CET1 fully loaded ratio
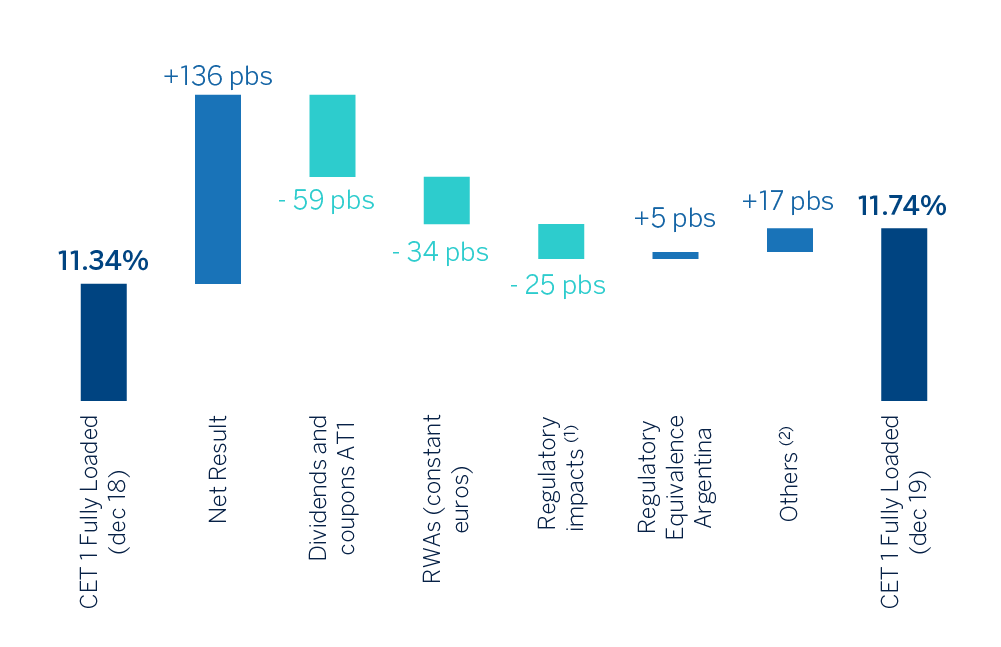
(1) Includes impacts of IFRS 16 (-11pbs) and TRIMs (-14pbs).
(2)Others mainly include the contribution of minority interests eligible as CET1 and market impacts, such as exchange rate impacts and evolution of the Held to Collect & Sell portfolio.
These levels are above the requirement established by the supervisor for 2019, and above the regulatory requirements applicable from January 1, 2020.
In November 2019, BBVA received a new communication from the Bank of Spain regarding its minimum requirement for own funds and eligible liabilities (MREL), as determined by the Single Resolution Board, that was calculated taking into account the financial and supervisory information as of December 31, 2017.
In accordance with such communication, BBVA has to reach, by January 1, 2021, an amount of own funds and eligible liabilities equal to 15.16% of the total liabilities and own funds of its resolution group, on sub-consolidated basis (the MREL requirement). Within this MREL, an amount equal to 8.01% of the total liabilities and own funds shall be met with subordinated instruments (the subordination requirement), once the relevant allowance is applied.
This MREL requirements equal to 28.50% in terms of risk-weighted assets (RWAs), while the subordination requirement included in the MREL requirement is equal to 15.05% in terms of RWAs, once the relevant allowance has been applied.
In order to comply with this requirement, BBVA has continued its program during 2019 by closing three non-preferred debt, for a total of €3.0 billion, of which one in green bonds by €1.0 billion. In addition, BBVA issued a senior preferred debt of €1.0 billion. Moreover, during the first two months of 2020, BBVA has issued a senior non-preferred debt of €1.25 billion euros and another of 160 million Swiss francs. The Group estimates that the current own funds and eligible liabilities structure of the resolution group meets the MREL requirement, as well as the new subordination requirement.
For its part, Risk-weighted assets (RWAs) increased by approximately €16.1 billion in 2019 as a result of activity growth, mainly in emerging markets and the incorporation of regulatory impacts (the application of IFRS 16 standard and TRIM - Targeted Review of Internal Models) for approximately €7.6 billion (which have had an impact on the CET1 ratio of -25 basis points). It should be noted that during the second quarter of the year the recognition by the European Commission of Argentina as a country whose supervisory and regulatory requirements are considered equivalent4 had a positive effect on the evolution of the RWAs.
The characteristics of the main capital instruments are shown in Annex III, available on the Group's website, in accordance with Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) No 1423/2013 of December 20, 2013.
The process of reconciliation between accounting own funds and regulatory own funds is shown below. Based on the shareholders’ equity reported in the Group’s Consolidated Financial Statements and applying the deductions and adjustments shown in the table below, we arrive at the regulatory capital figure eligible for solvency purposes:
Reconciliation of the Public Balance Sheet from the accounting perimeter to the regulatory perimeter
Million Euros
| Eligible capital own funds | 12-31-2019 | 12-31-2018 (2) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital | 3,267 | 3,267 |
| Share premium | 23,992 | 23,992 |
| Retained earnings, revaluation reserves and other reserves | 26,277 | 23,021 |
| Other equity | 56 | 50 |
| Less: Treasury shares | (62) | (296) |
| Attributable to the parent company | 3,512 | 3,400 |
| Attributed dividend | (1,084) | (1,109) |
| Total Equity | 55,958 | 54,326 |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (Loss) | (7,235) | (7,215) |
| Non-controlling interest | 6,201 | 5,764 |
| Shareholders' equity | 54,925 | 52,874 |
| Goodwill and other Intangible assets | (6,803) | (8,199) |
| Direct and synthetic treasury shares | (422) | (135) |
| Deductions | (7,225) | (8,334) |
| Differences from solvency and accounting level | (215) | (176) |
| Equity not eligible at solvency level | (215) | (176) |
| Other adjustments and deductions | (3,832) | (4,049) |
| Common Equity Tier 1 (CET 1) | 43,653 | 40,313 |
| Additional Tier 1 before Regulatory Adjustments | 6,048 | 5,634 |
| Tier 1 | 49,701 | 45,947 |
| Tier 2 | 8,304 | 8,756 |
| Total Capital (Tier 1 + Tier 2) | 58,005 | 54,703 |
| Total minimum capital required (1) | 46,540 | 41,576 |
- (1) Calculated over the minimum total capital applicable at each period.
- (2) As a result of the amendment to IAS 12 "Income Tax" as explained in Note 2.3 of the Group's Consolidated Financial Statements, and in order to make the information comparable, the information for the 2018 financial year has been restated, with no impact on either consolidated equity or regulatory capital.
- (3) Other adjustments and deductions include non-eligible minority amounts, distributed dividends pending payment and other deductions and prudential filters established by the CRR.
Following the guidelines of the EBA (EBA/GL/2018/01), the following is a summary of shareholders’ funds, capital adequacy ratios, leverage ratio with and without the application of the transitional provisions of IFRS 9 or the analogous ECL.
IFRS 9-FL - Comparison of institutions’ own funds and capital and leverage ratios with and without the application of transitional arrangements for IFRS 9 or analogous ECLs
Million Euros
| Own funds | 12-31-2019 | 09-30-2019 | 06-30-2019 | 03-30-2019 | 03-31-2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CET1 Capital | 43,653 | 43,432 | 42,329 | 41,784 | 40,313 |
| CET1 Capital without IFRS9 transitional arrangement or similar ECL | 42,844 | 42,623 | 41,520 | 40,975 | 39,449 |
| Tier 1 Capital (T1) | 49,701 | 51,035 | 48,997 | 47,455 | 45,947 |
| Tier 1 Capital (T1) without IFRS9 transitional arragement or similar ECL | 48,892 | 50,226 | 48,118 | 46,646 | 45,083 |
| Total Capital | 58,005 | 59,731 | 56,941 | 54,797 | 54,703 |
| Total Capital without IFRS9 transitional arragement or similar ECL | 57,196 | 58,922 | 56,132 | 53,988 | 53,839 |
| Risk-weighted assets (million euros) | |||||
| Total Risk-weighted assets | 364,448 | 368,196 | 360,069 | 360,679 | 348,264 |
| Total Risk-weighted assets without IFRS9 transitional arrangement or similar ECL | 364,943 | 368,690 | 360,563 | 360,173 | 348,804 |
| Capital ratio | |||||
| CET1 Capital (as a percentage of total exposure to risk) | 11.98% | 11.80% | 11.76% | 11.58% | 11.58% |
| CET1 Capital (as a percentage of total exposure to risk) without IFRS9 transitional arrangement or similar ECL | 11.74% | 11.56% | 11.52% | 11.35% | 11.31% |
| Tier 1 Capital (T1) (as a percentage of total exposure to risk) without IFRS9 transitional arrangement or similar ECL | 13.64% | 13.86% | 13.61% | 12.16% | 13.19% |
| Tier 1 Capital (T1) (as a percentage of total exposure to risk) without IFRS9 transitional arrangement or similar ECL | 13.40% | 13.62% | 13.36% | 12.92% | 12.93% |
| Total Capital (as a percentage of total exposure to risk) | 15.92% | 16.22% | 15.81% | 15.19% | 15.71% |
| Total Capital (as a percentage of total exposure to risk) without IFRS9 transitional arrangement or similar ECL | 15.67% | 15.98% | 15.57% | 14.95% | 15.44% |
| Leverage Ratio | |||||
| Total exposure related to leverage ratio | 731,087 | 740,141 | 732,135 | 722,708 | 705,229 |
| Leverage Ratio | 6.80% | 6.90% | 6.69% | 6.57% | 6.51% |
| Leverage ratio without IFRS9 transitional arrangements or similar ECL | 6.70% | 6.79% | 6.58% | 6.45% | 6.39% |
Entity risk profile and Minimum capital requirements
The BBVA Group has a general risk management and control model (hereinafter, the “Model”) that is appropriate for its business model, its organization, the countries where it operates and its corporate governance system. This model allows the Group to carry out its activity within the risk management and control strategy and policy defined by the corporate bodies of BBVA and to adapt itself to a changing economic and regulatory environment, facing this management at a global level and aligned to the circumstances at all times. The Model establishes a suitable risk management system related to the risk profile and strategy of the entity.
The types of risk inherent in the business that make up the risk profile of the Group are as follows:
- Credit risk and dilution: Credit risk arises from the probability that one party to a financial instrument will fail to meet its contractual obligations for reasons of insolvency or inability to pay and cause a financial loss for the other party. This includes counterparty risk, issuer risk, liquidation risk and country risk.
- Counterparty risk: The credit risk corresponding to derivative instruments, repurchase and resale transactions, securities or commodities lending or borrowing transactions and deferred settlement transactions.
- Credit valuation adjustment (CVA) risk:. Its aim is to reflect the impact on the fair value of the counterparty’s credit risk, resulting from OTC derivative instruments which are not recognized credit derivatives for the purpose of reducing the amount of credit risk weighted exposure.
- Market risk: Market risk originates in the possibility that there may be losses in the value of positions held due to movements in the market variables that affect the valuation of financial products and assets in the trading book. This includes risk with respect to the position in debt and equity instruments, exchange rate risk and commodity risk.
- Operational risk: A risk that can cause losses due to human errors, inadequate or defective internal processes, inadequate conduct toward customers or markets, failures, interruptions, or deficiencies of systems or communications, inadequate management of data, legal risk and, finally, as a consequence of external events, including cyberattacks, fraud committed by third parties, natural disasters, and poor service provided by suppliers. This definition includes legal risk, but excludes strategic and/or business risk and reputational risk.
- Structural risks: This is divided into structural interest-rate risk (movements in market interest rates that cause changes in an entity’s net interest income and book value) and structural exchange-rate risk (exposure to variations in exchange rates originating in the Group’s foreign companies and in the provision of funds to foreign branches financed in a different currency from that of the investment).
- Liquidity risk: Risk of an entity having difficulties in duly meeting its payment commitments, or where, to meet them, it has to resort to funding under burdensome terms which may harm the Group’s image or reputation.
- Reputational risk: Considered to be the potential loss in earnings as a result of events that may negatively affect the perception of the Group’s different stakeholders.
The chart below shows the total risk-weighted assets broken down by type of risk (where credit risk encompasses counterparty risk) as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018:
Distribution of RWAs by risk type eligible in Pillar I
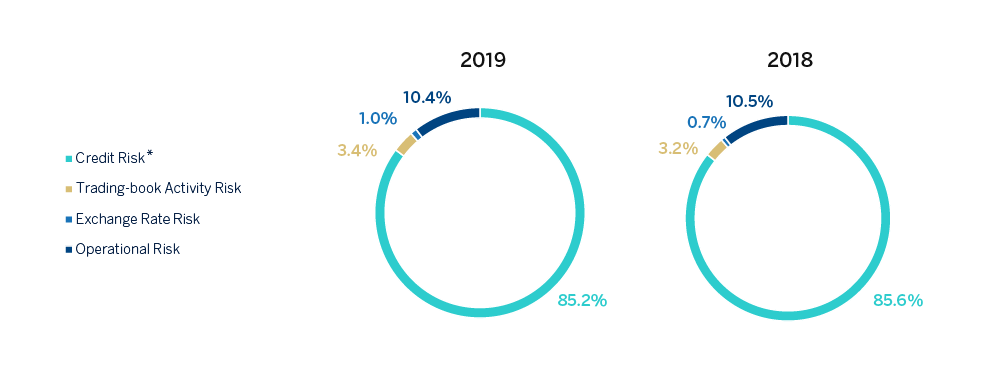
(*) Credit Risk includes Risk by CVA adjustment
The following table shows the total capital requirements broken down by risk type as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018:
EU OV1 - Overview of RWAs
| RWA's(1) | Minimum Capital requirements (2) (3) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 12-31-2019 | 12-31-2018 | 12-31-2019 | |
| Credit Risk (excluding CCR) | 286,159 | 274,256 | 22,893 |
| Of which th standarised approach(4) | 190,603 | 188,158 | 15,248 |
| Of which the foundation IRB (FIRB) approach(6) | 4,606 | 5,421 | 369 |
| Of which the advanced IRB (FIRB) approach(7) | 88,191 | 77,733 | 7,055 |
| Of which the foundation IRB (FIRB) approach(5) | 2,758 | 2,944 | 221 |
| CCR | 8,289 | 8,483 | 663 |
| Of which mark to market | 6,716 | 7,065 | 537 |
| Of which original exposure | - | - | - |
| Of which the standardised approach | - | - | - |
| Of which the internal model method (IMM) | - | - | - |
| Of which risk exposure amount for contributions to the default fund of a CCP | 44 | 41 | 3 |
| Of which CVA | 1,529 | 1,377 | 122 |
| Settlement Risk | - | - | - |
| Securitization exposures in the banking book (after the cap) | 924 | 2,623 | 74 |
| Of which IRB approach | 863 | 1,673 | 69 |
| Of which IRB supervisory formula approach(IAA) | - | - | - |
| Of which internal assessment approach (IAA) | - | - | - |
| Of which standardised approach | 61 | 950 | 5 |
| Market Risk | 16,066 | 13,316 | 1,285 |
| Of which standardised approach | 6,991 | 5,048 | 559 |
| Of which IMA | 9,075 | 8,268 | 726 |
| Operational risk | 37,877 | 36,725 | 3,030 |
| Of which basic indicator approach | 805 | 5,908 | 64 |
| Of which standardised approach | 15,250 | 9,341 | 1,220 |
| Of which IRB approach | 21,822 | 21,476 | 1,746 |
| Amounts below the thresholds for education (subject to 250% risk weight) | 15,134 | 12,862 | 1,211 |
| Floor adjustement | - | - | - |
| Total | 364,448 | 348,264 | 29,156 |
(1) Risk-weighted assets for the transitional period (phased-in)
(2) Calculated on 8% minimum total capital requirement (Article 92 of the CRR)
(3) Under CET1 requirements (9.27%) after the supervisory evaluation process (SREP), the requirements amount to 33,784 million euros. Under Total Capital requirements (12.77%), the requirements amount to 46,540 million euros.
(4) Deferred tax assets arising from temporary differences, which are not deducted from eligible own funds (subject to a risk weighting of 250%) are excluded, in accordance with Article 48.4 of the CRR. This amount is 7,279 and 6,548 as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively.
In addition, the standard method includes the impact of the first application of IFRS16 (for further information on the standard, see Note 2.3. of The Group's Consolidated Financial Statements).
(5) Equity, calculated under the simple risk-weighted approach and internal model method, is included. Significant investments in financial sector entities and insurers that are not deducted from eligible own funds (subject to a risk weighting of 250%) are excluded, in accordance with Article 48.4 of the CRR. This amount is 7,854 and 6,313 as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively.
(6) Exposure classified in the FIRB approach corresponds to specialized lending exposures. The Group has chosen to use the slotting criteria in line with Article 153.5 of the CRR.
(7) As of December 31, 2019, it includes the effects derived from TRIM (Targeted Review of Internal Models) that will become effective in 2020.
The evolution of RWAs during 2019 is characterized by the organic growth of the activity, being the effect of the exchange rate not relevant at this period. Additionally, the following singular impacts stand out:
- Inclusion of regulatory impacts (application of IFRS 16 and TRIM - Targeted Review of Internal Models) for approximately €7.6 billion.
- Recognition by the European Commission of Argentina as an equivalent country for the purposes of supervisory and regulatory requirements with a reduction in RWAs of approximately €1.5 billion.
- Change from basic method to standard method of operational risk at Garanti BBVA for the purpose of calculating consolidated requirements, which has resulted in a reduction of approximately €0.6 billion.
- Recognition of sovereign guarantees that mitigate the credit risk of securitizations, mainly from the United States, which has led to a reduction of approximately €0.9 billion.
The respective sections of the report explain in more detail the evolution of RWAs by type of risk.
The following is a breakdown of risk-weighted assets and capital requirements broken down by risk type and exposure categories as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018:
Capital requirements by risk type and exposure class
Million Euros
| Capital requirements (2) | RWA's (1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exposure Class and risk type | 12-31-2019 | 12-31-2018 | 12-31-2019 | 12-31-2018 |
| Credit Risk | 16,014 | 15,817 | 200,176 | 197,715 |
| Central goverments or central banks | 2,375 | 2,445 | 29,685 | 30,650 |
| Regional goverments or local authorities | 132 | 113 | 1,644 | 1,416 |
| Public sector entities | 63 | 57 | 790 | 714 |
| Multilateral development banks | 1 | 1 | 11 | 10 |
| International organisations | - | - | - | - |
| Institutions | 429 | 496 | 5,366 | 6,203 |
| Corporates | 6,999 | 7,159 | 87,486 | 89,481 |
| Retail | 3,079 | 2,941 | 38,493 | 36,768 |
| Secured by mortgages on immovable property | 1,199 | 1,237 | 14,983 | 15,466 |
| Exposures in default | 305 | 333 | 3,808 | 4,159 |
| Exposures associated with particularly high risk | 411 | 132 | 5,136 | 1,652 |
| Covered bonds | - | - | - | - |
| Claims on institutions and corporates with a short-term credit assesment | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Collective investments undertakings | 1 | 5 | 8 | 57 |
| Other exposures | 1,021 | 898 | 12,767 | 11,229 |
| Securitization exposures | 5 | 76 | 61 | 950 |
| Securitization exposures | 5 | 76 | 61 | 950 |
| Total credit risk by standardised approach | 16,019 | 15,893 | 200,237 | 198,665 |
| Credit Risk | 7,125 | 6,498 | 89,061 | 81,222 |
| Central goverments or central banks | 54 | 54 | 673 | 677 |
| Institutions | 532 | 429 | 6,646 | 5,336 |
| Corporates | 4,769 | 4,441 | 59,615 | 55,513 |
| Of which: SMEs | 998 | 950 | 12,478 | 11,877 |
| Of which: Specialised lending | 433 | 506 | 5,407 | 6,330 |
| Of which: Others | 3,338 | 2,984 | 41,730 | 37,305 |
| Retail | 1,770 | 1,573 | 22,128 | 19,667 |
| Of which: Secured by real estate property | 712 | 591 | 8,904 | 7,385 |
| Of which: Qualifying revolving | 589 | 555 | 7,365 | 6,938 |
| Of which: Other SMEs | 131 | 140 | 1,636 | 1,752 |
| Of which: Non-SMEs | 338 | 287 | 4,223 | 3,592 |
| Equity | 1,293 | 1,220 | 16,167 | 15,246 |
| On the basis of method: | - | - | ||
| Of which: Simple approach | 813 | 647 | 10,164 | 8,085 |
| Of which: PD/LGD approach | 444 | 479 | 5,554 | 5,989 |
| Of which: Intern models | 36 | 94 | 449 | 1,172 |
| On the basis of nature: | - | - | ||
| Of which: Listed instruments | 378 | 439 | 4,730 | 5,493 |
| Of which: Not listed instruments in sufficiently diversified portfolios | 915 | 780 | 11,437 | 9,753 |
| Securitization exposures | 69 | 134 | 863 | 1,673 |
| Securitization exposures | 69 | 134 | 863 | 1,673 |
| Total credit risk by IRB approach | 8,487 | 7,851 | 106,091 | 98,141 |
| Total contributions to the default fund of a ccp | 3 | 3 | 44 | 41 |
| Total credit risk | 24,510 | 23,748 | 306,372 | 296,846 |
| Settlement risk | - | - | - | - |
| Standardised approach: | 272 | 222 | 3,395 | 2,776 |
| Of which: Price Risk by fixed income exposures | 196 | 155 | 2,461 | 1,941 |
| Of which: Price Risk by Securitization exposures | 2 | 1 | 21 | 13 |
| Of which: Price Risk by correlation | 51 | 54 | 641 | 670 |
| Of which: Price Risk by stocks and shares | 20 | 11 | 24 | 18 |
| Of which: Commodities Risk | 2 | 1 | 24 | 18 |
| IRB: Market Risk | 726 | 661 | 9,075 | 8,268 |
| Total trading book risk | 998 | 884 | 12,470 | 11,044 |
| Foreing exchange risk (standardised approach) | 288 | 182 | 3,596 | 2,271 |
| CVA risk | 122 | 110 | 1,529 | 1,377 |
| Operational risk | 3,030 | 2,938 | 37,877 | 36,725 |
| Others (3) | 208 | - | 2,605 | - |
| Capital requirements | 29,156 | 27,861 | 364,448 | 348,448 |
(1) Risk-weighted assets according to the transitional period (phased-in).
(2) Calculated on the total capital requirements of 8% (Article 92 CRR).
(3) This line includes the regulatory impacts of TRIM (Targeted Review of Internal Models) which as of December 31, 2019 have not been assigned to their corresponding exposure category (mainly exposures guaranteed with real estate).
For more detail, see section 2 of the report.
3 This phased-in CET1 ratio takes into account the impact of the first implementation of the IFRS 9 standard. In this context, the Parliament and the European Commission have established transitional arrangements that are voluntary for the institutions, adapting the impact of IFRS 9 on capital ratios. The Group has informed the supervisory body of its adherence to these arrangements.
4 On April 1, 2019, the Official Journal of the European Union published Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2019/536, which includes Argentina within the list of third countries and territories whose supervisory and regulatory requirements are considered equivalent for the purposes of the treatment of exposures in accordance with Regulation (EU) No. 575/2013.
