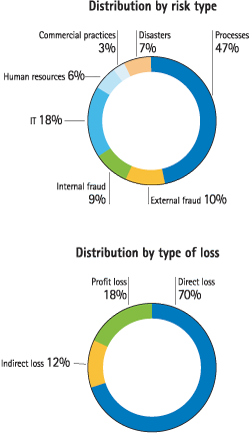Each business or support unit has one or more Internal Control and Operational Risk Committee (CIROC) that meet on a quarterly basis. These committees analyze the information provided by the tools and take the appropriate mitigation decisions. The measures adopted are then monitored to check their effectiveness.
Above these CIROC is the Country-level Committee for Internal Control and Operational Risk, which deals with more significant risks and their corresponding mitigation plans, as well as risks that cut across different areas.
Finally, there is a Global Committee for Internal Control and Operational Risk which carries out an overall monitoring of the Group’s main operational risks and also takes the most important decisions that at times may affect the whole Group or particular geographical area.
The corporate tools outlined below help provide a standardized view or risk, which within a short space of time has created a common language for the whole Organization.
Ev-Ro. Ev-Ro is a tool used to identify and prioritize operational risk factors, which are all those operational weaknesses that can generate losses. An analysis of the impact and frequency of each risk factor enables risk maps to be generated by business or support areas and class of risk.
The chart previous illustrates the distribution of risk by class and type of loss.
TransVaR. All the Group’s operations are based on process management. TransVaR is a key risk indicator (KRI) tool associated with processes. It identifies impairment or improvement in the Institution’s risk profile. Thus TransVaR is predictive in nature, because the indicators used are always associated with the causes that generate risk.
SIRO: Operational risk events nearly always have a negative impact on the Group’s income statement. To keep these events under control, they are recorded in a database called SIRO. To ensure reliability, 95% of its inputs are fed directly from accounting through automatic interfaces. The internal SIRO data are supplemented with information from an external database at the Operational Risk Exchange (ORX) consortium (orx@org.com). ORX is a non-profit association founded by 12 international banks in 2002, which currently has 55 members. BBVA is one of its founding partners.
The operational risk events are classified according to the risk classes established by Basel II: processes, fraud (internal and external), IT, human resources, commercial practices and disasters.
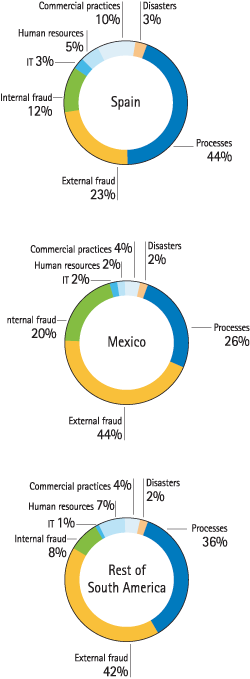
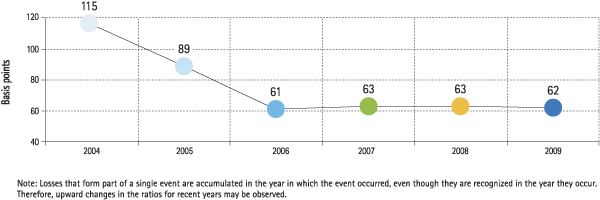
The following table shows the most significant losses suffered by the Group in 2009. Periodic monitoring is also carried out on the historical distribution of losses by geographical area and class of risk, as well as how they compare over time with the Group’s gross income. The accompanying charts show the results of this monitoring for the year.